Liver Cancer
Hepatocellular carcinoma is the main liver cancer that occurs most frequently. (HCC). Hepatocellular carcinoma is most common in individuals with chronic liver conditions like cirrhosis brought on by hepatitis B or C infection. People with cirrhosis or non-alcohol associated fatty liver should have regular hepatocellular carcinoma screenings.
Hepatocellular carcinoma usually grows slowly at first, but as the condition worsens, it may grow more quickly.
Signs and Symptoms:
Hepatocellular carcinoma symptoms can be caused by a number of different conditions; however, this does not necessarily indicate you have the disease. Hepatocellular carcinoma signs include:
- Unintentional weight loss
- Vomiting and Nausea
- A fullness or knot under your right-side rib, which denotes an enlarged liver
- Loss of appetite or sensation of fullness right after eating
- A feeling of fullness under your left side of the ribcage, indicating an enlarged spleen.
- Abdominal or right shoulder blade discomfort
- An enlarged stomach due to a fluid buildup
- Eyes turning sallow or yellow, which could be a symptom of jaundice
- Itchy skin
Diagnosis:
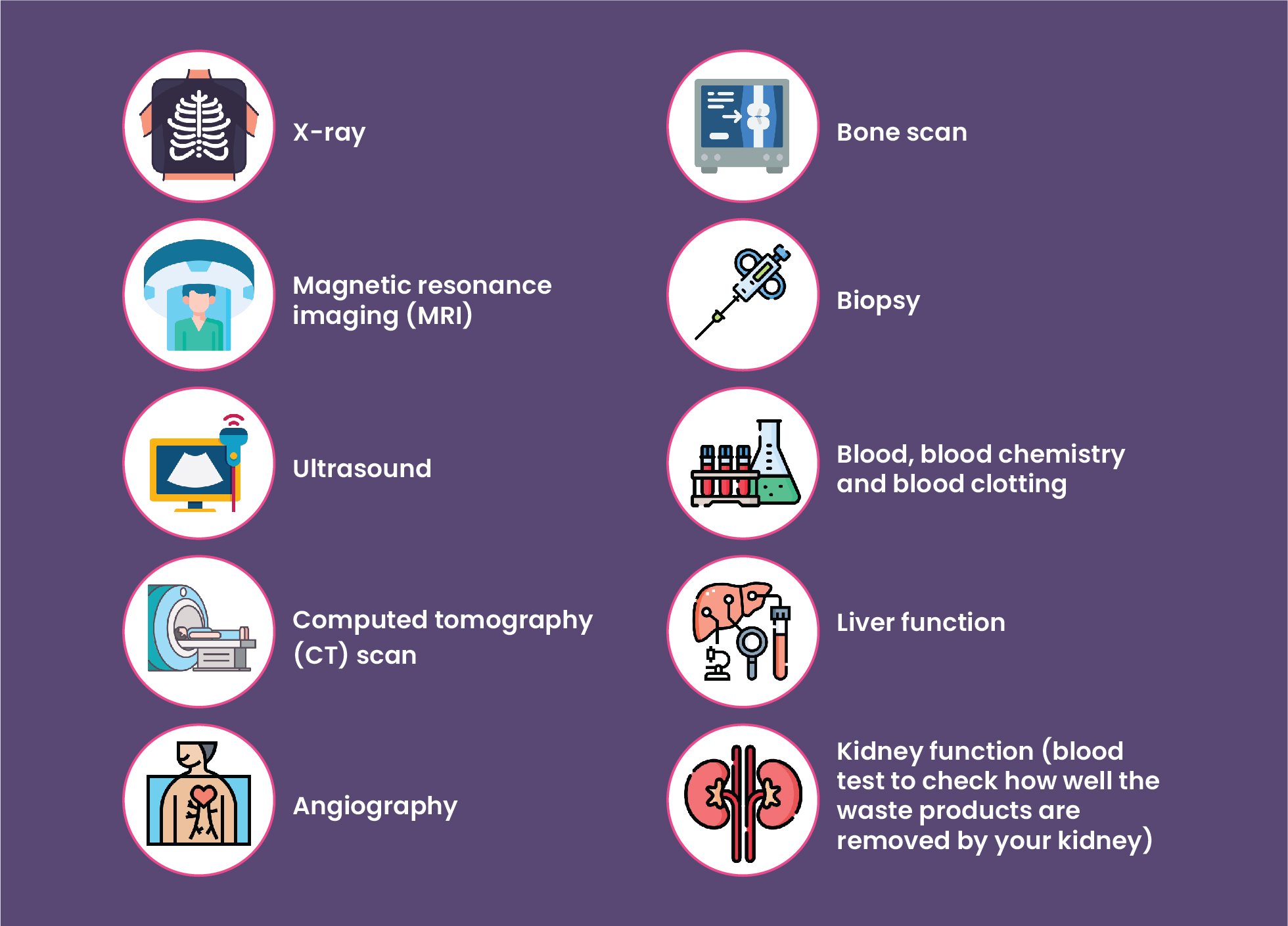
The following list includes the different tests and techniques that can be used to diagnose hepatocellular carcinoma:
- X-ray
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Ultrasound
- Computed tomography (CT) scan
- Angiography
- Bone scan
- Biopsy
- Blood, blood chemistry and blood clotting
- Liver function
- Kidney function (blood test to check how well the waste products are removed by your kidney)
Treatment
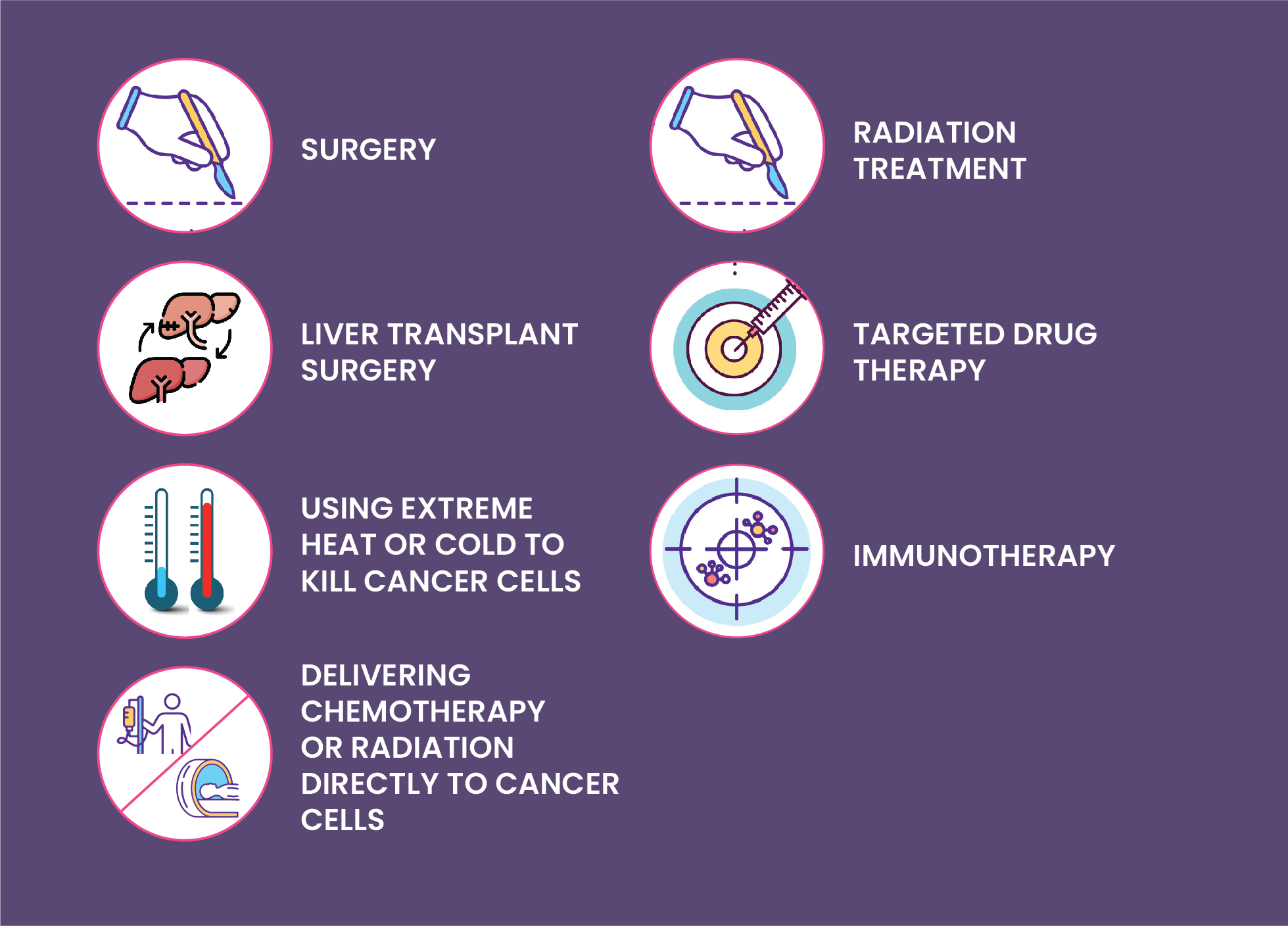
The best course of action will rely on the extent and location of the hepatocellular carcinoma, the health of the liver, and other factors. The therapies consist of:
- Surgery: Patients with early-stage liver cancer whose liver processes appear to be normal undergo surgery to remove the cancer and some of the surrounding tissues.
- Using extreme heat or cold to kill cancer cells: The ablation process kills liver cancer cells by using heat or cold to an extreme degree. For those who are unable to have surgery, it is performed. These include cryoablation, RF ablation, and microwave or alcohol-based ablation.
- Delivering chemotherapy or radiation directly to cancer cells: In this procedure, a catheter is passed through the blood vessel into the liver, so that chemotherapeutic drugs (chemoembolization) or tiny glass spheres containing radiations (radioembolization) can be directly delivered into cancer cells.
- Radiation treatment: Radiation therapy, which uses energy from X-rays or protons, can be used if surgery is not an option. Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) is a specific form of radiation treatment that involves focusing multiple radiation beams simultaneously at one location on the body.
- Liver transplant surgery: This process involves removing the entire liver and replacing it with a donor liver.
- Targeted drug therapy: Patients with advanced cancer may be treated with targeted drugs, which help to delay the disease's progression by going after specific vulnerabilities in cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: This method of managing advanced liver cancer uses your body's built-in immune response to infection to fight cancer cells.